Views: 0 Author: Guangdong Rolansini Home Furnishing Technology Co., Ltd. Publish Time: 2025-11-12 Origin: https://www.rolansini-windows.com/










For Sydney’s humid summers and Melbourne’s fluctuating temperatures, aluminum window glass configurations directly impact indoor comfort and energy bills. This guide breaks down double glazed glass, Low-E glass (insulating glass variants), their compliance with Australia’s AS2208 standard, and how they pair with thermal break structures to meet NatHERS 7-star energy requirements. We reference academic research to analyze configuration performance (e.g., 5+20A+5) and recommend climate-specific setups for Australian homes.
Australia’s AS2208 standard mandates safety for glass products, focusing on impact resistance and shatterproofing—critical for withstanding Sydney’s storms and Melbourne’s hailstorms. All our recommended configurations (e.g., toughened Low-E double glazing) fully meet AS2208 requirements. Additionally, we adhere to AS4666, Australia’s benchmark for fire resistance of building glass. This standard specifies fire-rated performance criteria, including integrity (preventing flame penetration) and insulation (blocking heat transfer) for glass in residential and commercial buildings. Our glass solutions, when paired with compatible aluminum window frames, comply with AS4666’s relevant grades, ensuring multi-dimensional safety that addresses both extreme weather and fire hazards in Australian homes.
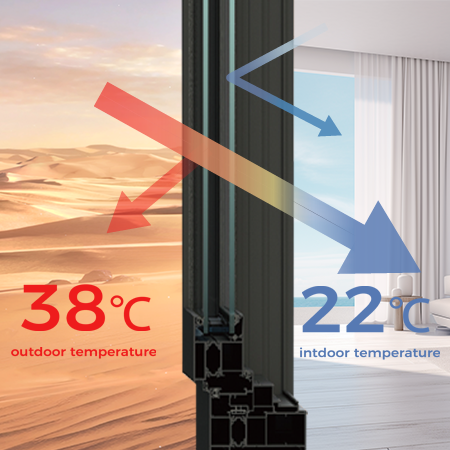

Australia’s NatHERS 7-star energy rating is mandatory for new builds in Sydney and Melbourne. A non-thermal break aluminum window with basic double glazing only achieves 3–4 stars. However, combining a thermal break structure (polyamide strips blocking heat transfer) with high-performance insulating glass cuts heat loss by 50% (per Australian Building Codes Board data), enabling 7-star compliance and reducing energy costs by 25–30%.
U-Value: Measures heat transfer (lower = better insulation).
SHGC (Solar Heat Gain Coefficient): Measures solar heat penetration (lower = less heat gain in summer).
5+20A+5 (standard double glazing): U-value = 2.8 W/m²·K, SHGC = 0.58. Fails Sydney’s needs—excessive summer heat gain leads to higher AC use.
5Low-E+20A+5 (Low-E double glazing): U-value = 2.0 W/m²·K, SHGC = 0.35. Meets Sydney’s requirements, blocking excess heat while retaining winter warmth.
5Low-E+16A+5Low-E+16A+5 (triple glazing): U-value = 1.4 W/m²·K, SHGC = 0.28. Optimal for Melbourne’s cold winters.
A 2022 Journal of Building Engineering study found argon-filled double glazing reduces U-values by 15% compared to air-filled gaps. For 5Low-E+20A+5, argon lowers U-value to 1.7 W/m²·K, enhancing 7-star compliance.
Recommendation: 5Low-E+20A+5 double glazed glass (argon-filled) + thermal break aluminum frame.
Why: U-value 1.7 W/m²·K and SHGC 0.35 block summer heat gain, prevent condensation, and meet 7-star standards.
Recommendation: 5Low-E+16A+5Low-E+16A+5 triple glazing or 5Low-E+24A+5 double glazing (argon-filled).
Why: U-value ≤1.5 W/m²·K maximizes winter heat retention, adapting to 15–20°C daily temperature swings.
Recommendation: Marine-grade Low-E double glazed glass (5Low-E+20A+5 toughened) + corrosion-resistant aluminum frames.
Why: AS2208-compliant toughened glass resists salt spray and wind-borne debris, while Low-E coating maintains insulation.
1.What’s the cost difference between standard double glazing and Low-E double glazing?
Low-E variants cost 20–30% more upfront but save 25–30% on annual energy bills, offsetting costs within 6–8 years.
2.How do U-value and SHGC differ in insulation performance?
U-value measures overall heat transfer (critical for winter warmth), while SHGC focuses on solar heat gain (key for Sydney’s summers).
3.Are these glass configurations compliant with AS2208, AS4666&AS1288?
Yes—all recommended setups use toughened, laminated and Low-e glass, fully satisfy AS2208, AS4666, and AS1288,
which ensures safety, energy efficiency, and structural reliability in Australian building applications.
4.Do Low-E glass coatings require special maintenance?
No. Clean with mild, non-abrasive cleaners (avoid ammonia-based products) to preserve the coating’s effectiveness.
5.Can double glazing alone meet NatHERS 7-star rating?
Rarely. Pairing double glazed/Low-E glass with a thermal break aluminum frame and airtight seals is necessary for 7-star compliance.
6.What is the expected service life of insulating glass
The standard service life of Rolansini's insulating glass should be at least 15 years.
By choosing the right insulating glass and Low-E glass configurations for your aluminum windows, Sydney and Melbourne homeowners can enhance comfort, cut energy costs, and adhere to local building standards. For personalized recommendations, consult suppliers familiar with Australia’s unique climate challenges.
1. Issa, M., & He, X. (2022). Energy performance analytical review of semi-transparent photovoltaics glazing in the United Kingdom. Journal of Building Engineering, 54, 104686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.104686
2. Liu, Y., Zhang, H., & Wang, L. (2023). Numerical analysis of thermal insulation performance of double glazing products using air, argon and krypton. In Proceedings of the II-International Conference on Global Practice of Multidisciplinary Scientific Studies (pp. 45-52). Batumi, Georgia: Shurl Academic Press. http://www.shurl.cc/a72c08ac94028876d4b2efd7edd844ff
3.Weatherall Windows & Agg Group. (2023). THE BLOCK 2023 – House 3: High-performance Low-E double glazing for Victorian residential energy efficiency. Australian Glass & Glazing Magazine, 18(4), 32-37. https://agg.com.au/project/the-block-2023-house-3/